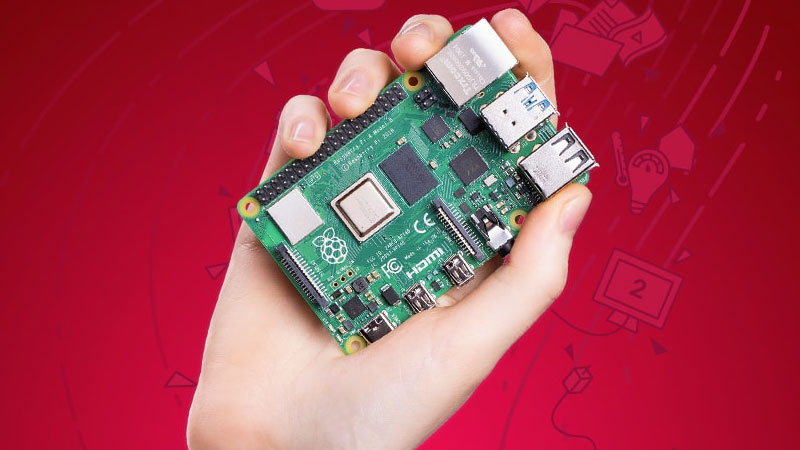
Introduction
The Raspberry Pi is a compact, affordable single-board computer designed to make computing accessible and encourage learning in programming, electronics, and hardware development. About the size of a credit card, it packs the functionality of a desktop computer—supporting operating systems, internet connectivity, USB devices, and HDMI displays—while offering unique features like GPIO pins for connecting sensors, motors, and other components. Originally developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation to promote computer science education, it has grown into a versatile platform used for everything from DIY electronics and robotics to home automation, media centers, and even small-scale servers. Its low cost, open-source ecosystem, and flexibility make it a favorite among students, hobbyists, and engineers worldwide.
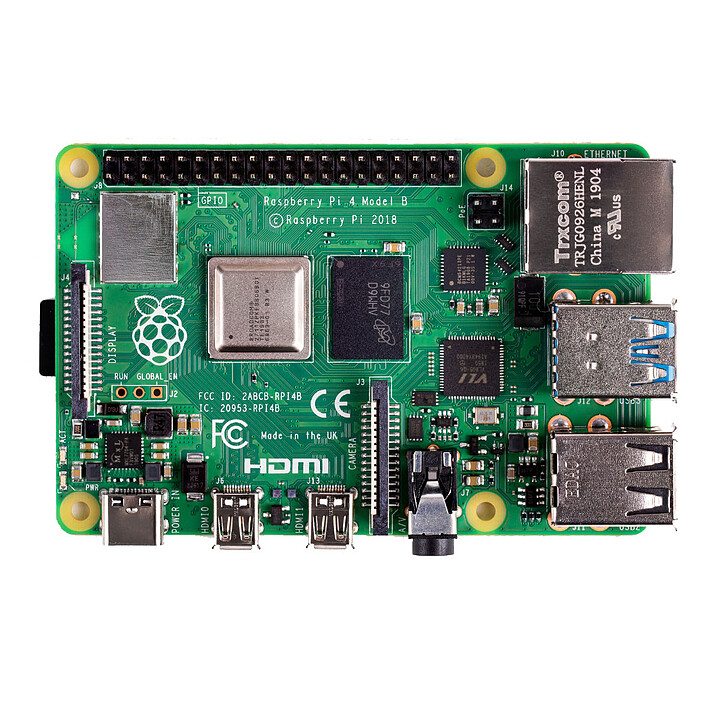
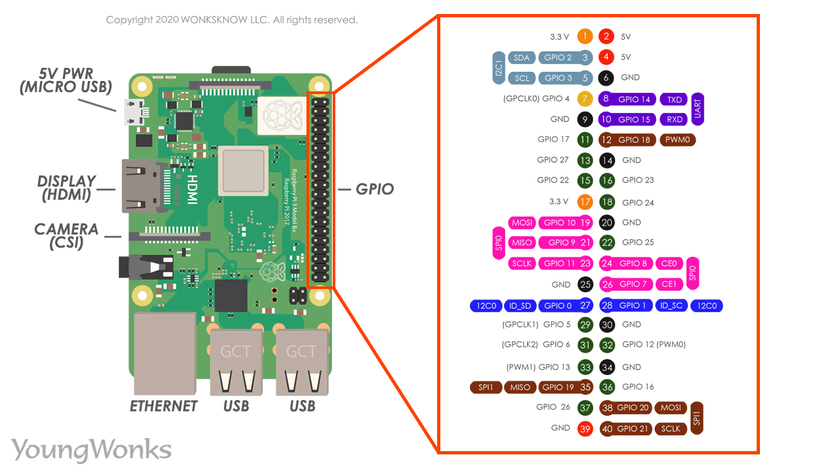
This standardized 40-pin GPIO header, present on Raspberry Pi 2, 3, 4, and similar models, includes power pins (3.3 V, 5 V), numerous grounds, and configurable GPIO pins capable of supporting I²C, SPI, UART, PWM, and PCM interfaces
Pin assignments are consistent across these models, with the first generation Pi (Model A/B Rev 1) using only the first 26 pins
The pin numbering conventions—Physical Pin vs. BCM (Broadcom GPIO)—are vital when programming; for instance, GPIO 18 corresponds to physical pin 12
Architecture Diagram
This block-level diagram outlines the major hardware elements found on a typical Raspberry Pi (Model B series), including:
- Processor/SoC: Usually a Broadcom chip like BCM2835 (Pi 1), BCM2837 (Pi 3), or BCM2711 (Pi 4)
- GPU: VideoCore series (IV on earlier models, VI on Raspberry Pi 4) for graphics and multicore multimedia capabilities
- I/O Interfaces: HDMI, USB ports, Ethernet (on Model B), audio output, camera (CSI) and display (DSI) connectors, SD card slot, and power input via micro USB or USB-C (on newer models)
Common use case of Raspberry pi
The Raspberry Pi is widely used for learning programming, building electronics projects, and creating practical low-cost computing solutions. Students and hobbyists use it to learn Python, C, and other languages, while makers often take advantage of its GPIO pins to build robots, control sensors, or automate devices. It’s also popular for home automation, serving as the brain for smart lighting, security cameras, and IoT systems. With media software like Kodi or RetroPie, it transforms into a streaming box or retro gaming console, and many people use it as a personal server, VPN, or private cloud. Beyond personal projects, engineers and researchers use Raspberry Pi for rapid prototyping, edge AI tasks, and small-scale data collection, making it a flexible platform for education, innovation, and real-world applications.
All the models you can get
| Series / Model | Release Year | Key Specs / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Original Series | ||
| Raspberry Pi Model B | 2012 | 700 MHz ARM11 CPU, 512 MB RAM, 26-pin GPIO |
| Raspberry Pi Model A | 2013 | 256 MB RAM, no Ethernet |
| Raspberry Pi Model B+ | 2014 | 40-pin GPIO, 4× USB ports, 512 MB RAM |
| Raspberry Pi Model A+ | 2014 | 256 MB/512 MB RAM, smaller size |
| Second Generation | ||
| Raspberry Pi 2 Model B | 2015 | Quad-core 900 MHz CPU, 1 GB RAM |
| Third Generation | ||
| Raspberry Pi 3 Model B | 2016 | 1.2 GHz quad-core CPU, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth |
| Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ | 2018 | 1.4 GHz CPU, faster Ethernet, dual-band Wi-Fi |
| Raspberry Pi 3 Model A+ | 2018 | 1.4 GHz CPU, 512 MB RAM, small board |
| Fourth Generation | ||
| Raspberry Pi 4 Model B | 2019 | Quad-core 1.5 GHz CPU, 1–8 GB RAM, USB-C power, dual HDMI |
| Fifth Generation | ||
| Raspberry Pi 5 | 2023 | Quad-core 2.4 GHz CPU, PCIe support, 4 GB or 8 GB RAM |
| Zero Series | ||
| Raspberry Pi Zero | 2015 | Ultra-small, 1 GHz CPU, 512 MB RAM |
| Raspberry Pi Zero W | 2017 | Adds Wi-Fi and Bluetooth |
| Raspberry Pi Zero WH | 2018 | Pre-soldered GPIO header |
| Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W | 2021 | Quad-core CPU, 512 MB RAM, Wi-Fi |
| Compute Module Series | ||
| Compute Module 1 | 2014 | Based on Model A+, for embedded designs |
| Compute Module 3 | 2017 | Based on Pi 3 CPU, more memory |
| Compute Module 3+ | 2019 | Thermal improvements |
| Compute Module 4 | 2020 | Based on Pi 4, multiple RAM/flash options |
| Compute Module 4S | 2022 | Pi 4 on CM3-sized board |
| Special Boards | ||
| Raspberry Pi 400 | 2020 | Pi 4 built into a keyboard |
| Raspberry Pi Pico | 2021 | RP2040 microcontroller, no Linux |
| Raspberry Pi Pico W | 2022 | Pico with built-in Wi-Fi |

